Linux命令之lsblk命令
一、命令简介
lsblk命令的英文是“list block”,即用于列出所有可用块设备的信息,而且还能显示他们之间的依赖关系,但是它不会列出RAM盘的信息。块设备有硬盘,闪存盘,CD-ROM等等。lsblk命令包含util-linux中。通过yum provides lsblk命令查看命令对应的软件包。
不通的版本命令参数可能略有差异,此博文示例环境说明:
1.操作系统:centos 7.6。
2.lsblk命令版本:2.23.2。
二、使用示例
1、获取命令帮助 :
[root@test1 ~]# lsblk –help
Usage:
lsblk [options] [<device> …]
List information about block devices.
Options:
-A, –noempty don’t print empty devices
-D, –discard print discard capabilities
-E, –dedup <column> de-duplicate output by <column>
-I, –include <list> show only devices with specified major numbers
-J, –json use JSON output format
-M, –merge group parents of sub-trees (usable for RAIDs, Multi-path)
-O, –output-all output all columns
-P, –pairs use key=”value” output format
-S, –scsi output info about SCSI devices
-N, –nvme output info about NVMe devices
-v, –virtio output info about virtio devices
-T, –tree[=<column>] use tree format output
-a, –all print all devices
-b, –bytes print SIZE in bytes rather than in human readable format
-d, –nodeps don’t print slaves or holders
-e, –exclude <list> exclude devices by major number (default: RAM disks)
-f, –fs output info about filesystems
-i, –ascii use ascii characters only
-l, –list use list format output
-m, –perms output info about permissions
-n, –noheadings don’t print headings
-o, –output <list> output columns
-p, –paths print complete device path
-r, –raw use raw output format
-s, –inverse inverse dependencies
-t, –topology output info about topology
-w, –width <num> specifies output width as number of characters
-x, –sort <column> sort output by <column>
-y, –shell use column names to be usable as shell variable identifiers
-z, –zoned print zone related information
--sysroot <dir> use specified directory as system root
-h, –help display this help
-V, –version display version
Available output columns:
ALIGNMENT alignment offset
ID-LINK the shortest udev /dev/disk/by-id link name
ID udev ID (based on ID-LINK)
DISC-ALN discard alignment offset
DAX dax-capable device
DISC-GRAN discard granularity
DISK-SEQ disk sequence number
DISC-MAX discard max bytes
DISC-ZERO discard zeroes data
FSAVAIL filesystem size available
FSROOTS mounted filesystem roots
FSSIZE filesystem size
FSTYPE filesystem type
FSUSED filesystem size used
FSUSE% filesystem use percentage
FSVER filesystem version
GROUP group name
HCTL Host:Channel:Target:Lun for SCSI
HOTPLUG removable or hotplug device (usb, pcmcia, …)
KNAME internal kernel device name
LABEL filesystem LABEL
LOG-SEC logical sector size
MAJ:MIN major:minor device number
MIN-IO minimum I/O size
MODE device node permissions
MODEL device identifier
MQ device queues
NAME device name
OPT-IO optimal I/O size
OWNER user name
PARTFLAGS partition flags
PARTLABEL partition LABEL
PARTN partition number as read from the partition table
PARTTYPE partition type code or UUID
PARTTYPENAME partition type name
PARTUUID partition UUID
PATH path to the device node
PHY-SEC physical sector size
PKNAME internal parent kernel device name
PTTYPE partition table type
PTUUID partition table identifier (usually UUID)
RA read-ahead of the device
RAND adds randomness
REV device revision
RM removable device
RO read-only device
ROTA rotational device
RQ-SIZE request queue size
SCHED I/O scheduler name
SERIAL disk serial number
SIZE size of the device
START partition start offset
STATE state of the device
SUBSYSTEMS de-duplicated chain of subsystems
MOUNTPOINT where the device is mounted
MOUNTPOINTS all locations where device is mounted
TRAN device transport type
TYPE device type
UUID filesystem UUID
VENDOR device vendor
WSAME write same max bytes
WWN unique storage identifier
ZONED zone model
ZONE-SZ zone size
ZONE-WGRAN zone write granularity
ZONE-APP zone append max bytes
ZONE-NR number of zones
ZONE-OMAX maximum number of open zones
ZONE-AMAX maximum number of active zones
For more details see lsblk(8).
2、查看命令版本:[root@test1 ~]# lsblk -V
lsblk from util-linux 2.23.2
3、列表所有块设备:[root@test1 ~]# lsblk -a
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 40G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 300M 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 2G 0 part [SWAP]
└─sda3 8:3 0 37.7G 0 part /
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
4、查看scsi信息:[root@test1 ~]# lsblk -S
NAME HCTL TYPE VENDOR MODEL REV TRAN
sda 0:0:0:0 disk VMware, VMware Virtual S 1.0 spi
sr0 2:0:0:0 rom NECVMWar VMware IDE CDR10 1.00 ata
5、查看指定块设备信息:[root@test1 ~]# lsblk /dev/sda1
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda1 8:1 0 300M 0 part /boot
[root@test1 ~]# lsblk /dev/sda
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 40G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 300M 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 2G 0 part [SWAP]
└─sda3 8:3 0 37.7G 0 part /
6、查看块设备的文件系统类型及UUID:[root@test1 ~]# lsblk -f
NAME FSTYPE LABEL UUID MOUNTPOINT
sda
├─sda1 xfs 5f9fac01-fc0e-499e-8979-6d987bab5f5c /boot
├─sda2 swap 673d404e-08c9-433a-98ca-987720f1d9d1 [SWAP]
└─sda3 xfs 0be8e221-259d-4a5a-9b91-c1b792afde23 /
sr0
7、查看块设备的完整路径:[root@test1 ~]# lsblk -p
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
/dev/sda 8:0 0 40G 0 disk
├─/dev/sda1 8:1 0 300M 0 part /boot
├─/dev/sda2 8:2 0 2G 0 part [SWAP]
└─/dev/sda3 8:3 0 37.7G 0 part /
/dev/sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
8、以列表形式展示块设备:默认是以树的形式展示:[root@test1 ~]# lsblk -lp
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
/dev/sda 8:0 0 40G 0 disk
/dev/sda1 8:1 0 300M 0 part /boot
/dev/sda2 8:2 0 2G 0 part [SWAP]
/dev/sda3 8:3 0 37.7G 0 part /
/dev/sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
三、使用语法及参数说明
1、使用语法:
用法:lsblk [options] [<device>]
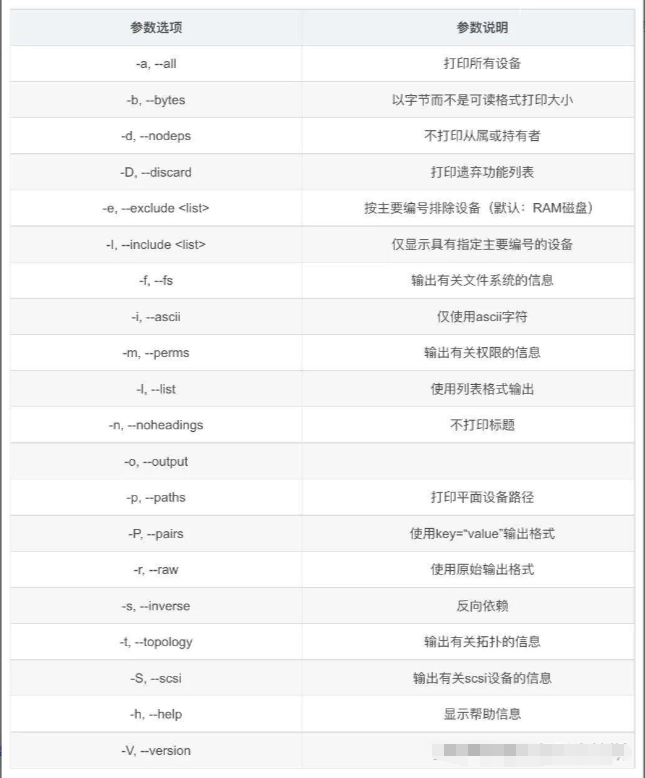
2、参数说明:
3、输出信息列说明: